Analyzing the Information by Means of Interactive Visualizations: User interaction with data is closely related to its visual representation. Interactive visualization technology displays numerous aspects of multidimensional data using interactive pictures and charts. The colour, size, shape and motion of objects represent the multidimensional aspects of the data. Information visualization has been defined as “the use of computer-supported, interactive, visual representations of abstract data to amplify cognition”. A good visual representation can amplify user cognition by providing more information, faster, with less cognitive effort. BI platform vendors are currently promoting these technologies as an alternative and enrichment to traditional reporting and online analytical processing capabilities. CUBIST will provide BI users with visualization and interaction techniques enhanced by Semantic Technologies, such as Formal Concept Analysis (FCA).
FCA captures hitherto undiscovered patterns in data. Concepts are formalised as groups of objects associated with groups of attributes. Hierarchical relationships between these groups are formed and visualized and can be used for information retrieval. Information organised in this way has a close correlation to human perception. Thus, FCA has been used as the basis for semantic search engines and as a means of organising information based on its meaning. FCA has also been used to mine data for groups of items and their associated transactions to identify, for example, groups of products that are frequently purchased together.
Objectives
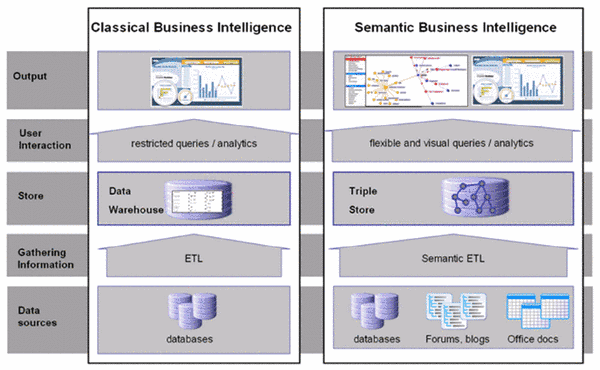
Objective 1: Semantic ETL. Unlike classical BI, CUBIST will provide comprehensive methods to bring unstructured data into analytics. SETL will use lineage information, metadata of data sources, semantic descriptions, and meaning of extracted data to support error detection within data sources and the SETL process. Semi-automated mapping of structured data sources to the RDF model will reduce the complexity of data integration. This objective will be approached by leveraging ETL best practises, orchestrated and wrapped by a semantic layer.
Expected Result: Semantically enriched lineage information, error detection within extracted data and CUBIST information warehouse and a SETL component that provides SPARQL endpoints for various data sources.
Objective 2: Semantic Warehouse. CUBIST will employ an RDF triple store and ontology as the backbone for the information warehouse, to improve performance and reduce the complexity of the integration of heterogeneous data sources. ST will enrich BI by enabling the discovery of new implicit information through logical reasoning. The standard RDF query language SPARQL will be extended by OLAP functionalities for complex aggregates and analysis. The information warehouse will use advanced indexing and materialisation techniques known from state-of-the-art data warehousing to improve the performance of the RDF triple store. A layer within the warehouse will integrate the triple store with the FCA-based visual analytics.
Expected Result: OLAP extensions for SPARQL, discovery mechanism for finding implicit information, triple store based information warehouse, integration of triple store with FCA.
Objective 3: FCA-Based Advanced Visual Analytics. On top of the Semantic Warehouse, CUBIST will provide ways to visualize and explore hitherto undiscovered BI using FCA.
Expected Result: High performance formal concept miner, large scale FCA capability, FCA visualization of BI.