



Next: Algebraic Systems.
Up: Overview of Capabilities.
Previous: Overview of Capabilities.
Contents
Summary.
AUTO can do a limited bifurcation analysis of algebraic systems
 |
(2.1) |
The main algorithms in AUTO, however, are aimed at the continuation
of solutions of systems of ordinary differential equation (ODEs) of the form
 |
(2.2) |
subject to boundary (including initial) conditions and integral constraints.
Above, 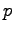 denotes one or more free parameters,
denotes one or more free parameters,
These boundary value algorithms also allow AUTO to do certain stationary
solution and wave calculations for the partial differential equation (PDE)
 |
(2.3) |
where 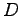 denotes a diagonal matrix of diffusion constants.
denotes a diagonal matrix of diffusion constants.
The basic algorithms used in AUTO,
as well as related algorithms, can be found in
HBK:77 HBK:77,
HBK:86 HBK:86,
DoKeKe:91a DoKeKe:91a,
DoKeKe:91b DoKeKe:91b.
Below, the basic capabilities of AUTO are specified in more detail.
Some representative demos are also indicated.




Next: Algebraic Systems.
Up: Overview of Capabilities.
Previous: Overview of Capabilities.
Contents
Gabriel Lord
2007-11-19